Time Series Forecasting with Graphical Models
Recently emerged Graph signal processing (GSP) techniques provide efficient ways to utilize geographical information. Previous time series models on graphs often construct graph structures through the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm with latitude and longitude data. Recent research has suggested that processing the graph data in the graph frequency domain provides better results.
Previous time series models on graphs seldom care about the non-stationary case. We propose the multivariate GARCH models on graphs (G-GARCH), which consider the relationship between geographical information and volatility. The G-GARCH model has the advantage of parameter saving if the data in the graph frequency domain are uncorrelated. Additionally, the G-GARCH model can be extended to the asymmetric case, like Graph Exponential GARCH (G-GARCH), and Graph GJR-GARCH (G-GJR-GARCH).
We have applied these Graph GARCH models into wind power forecasting and temperature forecasting, and achieved significant improvements compared to previous time series models. The results are shown in the following figures.
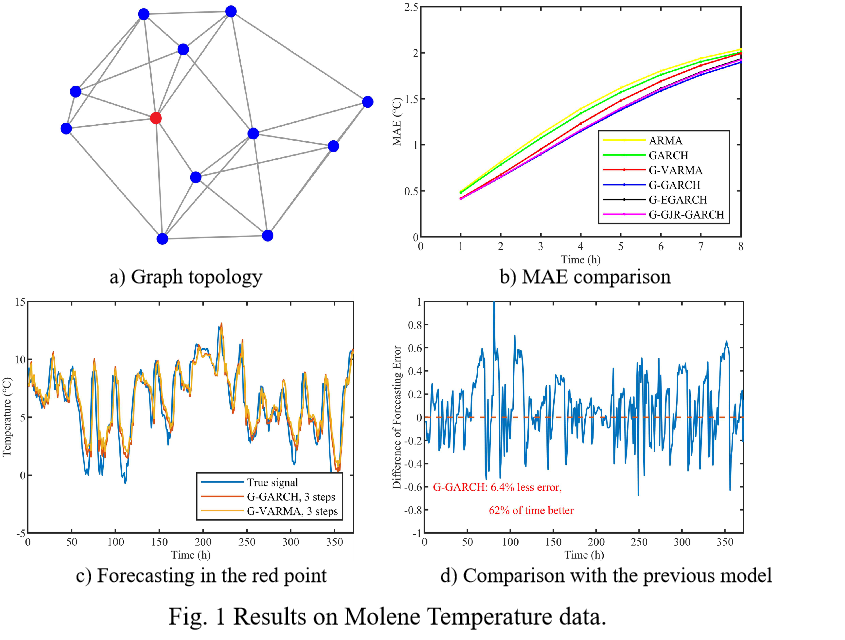 |
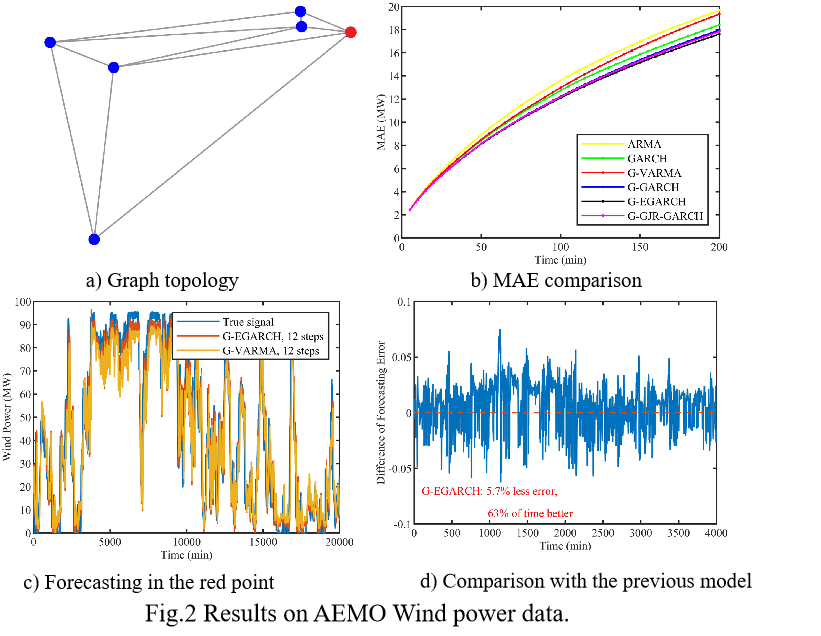 |
Reference
1. J. Hong, Y. Yi, E.E. Kuruoglu, and W.K.Chan, Multivariate Time Series Forecasting with GARCH Models on Graphs.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL AND INFORMATION PROCESSING OVER NETWORKS, under review.