Stochastic Graphs
Recently emerged Graph signal processing (GSP) techniques provide efficient solutions to deal with irregularly structured data. GSP techniques have already been applied in modeling brain functional connectivity, spatial temperature data, transportation flows, monitoring 5G signal strength, sensor networks in smart cities, structuring geometric data, and modeling transportation flows. The spectral analysis of GSP is the backbone of the Graph Convolutional Neural network, one of the most well-known graph deep learning architectures.
Efficient and robust online processing techniques for irregularly structured data are crucial in the current era of data abundance. Our current research on GSP focuses on the time-varying data that reside on the nodes of graphs. The graphs are corrupted by impulsive noise and have missing node observations. Even more, the irregularity of graph structures and the time-varying nature of data are extra layers of difficulty. To deal with these challenges, our research utilizes the GSP to process time-varying data in the graph Spectral domain and combines GSP with classical adaptive filters to process time-varying graph signals. Previous GSP algorithms assume the noise is Gaussian, A gross oversimplification that leads to often unstable estimations of real-world data; our research on GSP breaks the Gaussian noise assumption by using lp norm optimization instead of l2 norm optimization.
 |
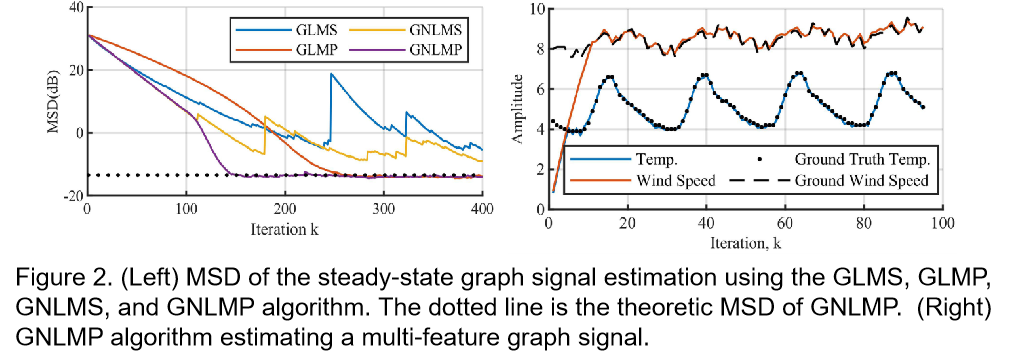
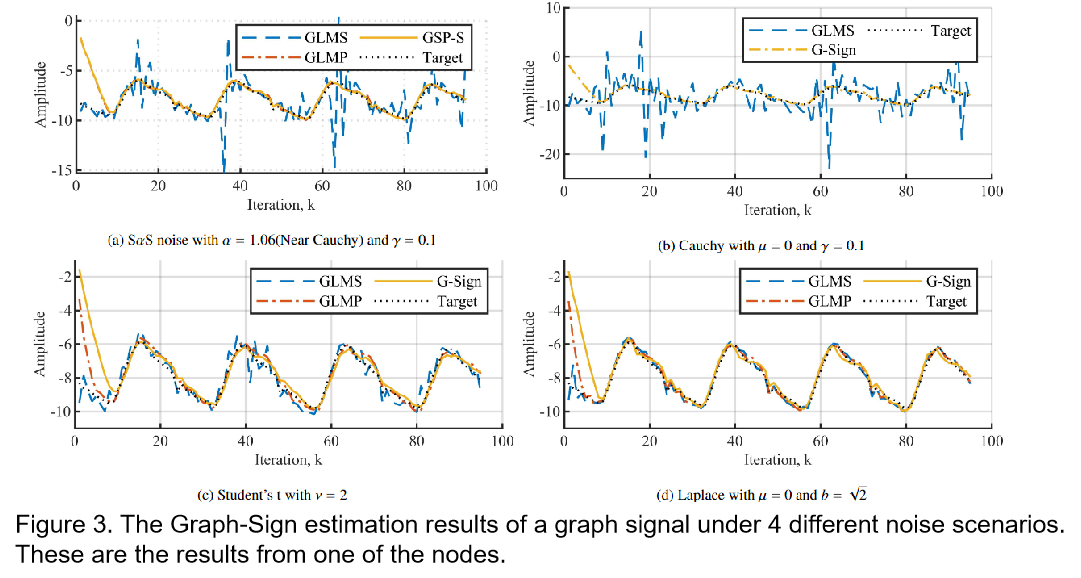
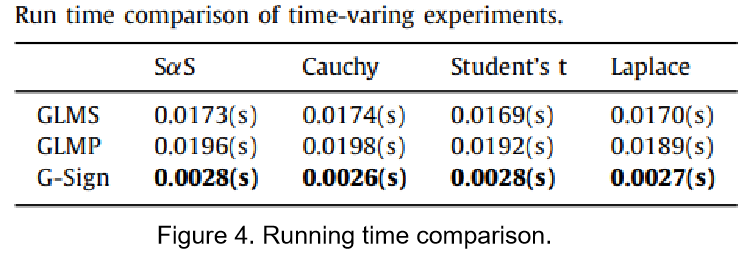
We proposed 2 adaptive graph algorithms, namely the graph Normalized least mean pth (GNLMP) algorithm and the Graph-Sign algorithm, that solves the aforementioned problems. The GNLMP algorithm has faster runtime compared to its unnormalized predecessor GLMP when estimating under alpha-stable noise without sacrificing accuracy. The Graph-Sign algorithm further reduces the computational complexity compared to the graph LMS (GLMS), which is the simplest adaptive GSP algorithm before the emergence of Graph-Sign. The Graph-Sign algorithm requires only 1/8 of the runtime compared to that of the graph LMS when estimating the same graph signal under noise. The Graph-Sign algorithm shows robust estimation performance on non-gaussian noise modeled using alpha-stable distribution, Cauchy distribution, student t’s distribution, and Laplace distribution.
 |
 |
 |
Reference
1. Y. Yan, R. Adel, and E.E. Kuruoglu, Graph Normalized-LMP Algorithm for Signal Estimation Under Impulsive Noise. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 2022, https:doi.org10.1007s11265-022-01802-2.
2. Y. Yan, E. E. Kuruoglu, and M. A. Altinkaya, “Adaptive sign algorithm for graph signal processing,” Signal Processing, Volume 200, 2022, 108662, https:doi.org10.1016j.sigpro.2022.108662.
3. Y. Yan, R. Adel, and E. E. Kuruoglu, “Adaptive Normalized LMP Estimation for Graph Signal Processing,” 2021 IEEE 31st International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), 2021, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/MLSP52302.2021.9596181.